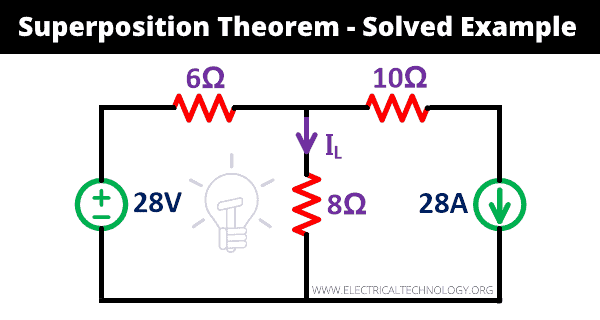
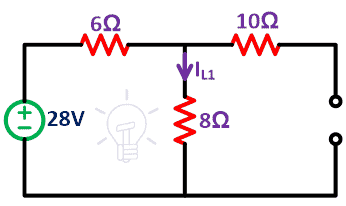
Source Transformation Technique (Voltage Source to Current Source & Current Source to Voltage Source)

- Source Transformation Definition: Source transformation is defined as a technique to simplify circuit analysis by converting between equivalent voltage and current sources using Thévenin’s and Norton’s theorems.
- Voltage to Current Conversion: This conversion involves calculating the current supplied by a shorted voltage source and connecting the same resistance across the current source.
- Current to Voltage Conversion: Converts a current source into a voltage source by applying Ohm’s law to determine the voltage across an open circuit.
- Circuit Simplification: Source transformation allows easier analysis and understanding of complex circuits by changing the type of sources without altering electrical behavior.
- Educational Resources: Additional learning materials, like video explanations, are available for those who prefer visual or auditory learning methods.
What is a Source Transformation?
Source transformation is a technique used to simplify an electric circuit.
We’ll illustrate how this is done with an example.
Let’s take a simple voltage source along with a resistance connected in series with it.
The series resistance in the diagram models the internal resistance typical of practical voltage sources.

Now, let us short circuit the output terminals of the voltage source circuit as shown below,


Applying Kirchhoff Voltage Law to the above circuit yields:

Where, I is the current delivers by the voltage source when it is short circuited.
Now, let’s take a current source of the same current I which produces same open-circuit voltage at its open terminals as shown below,

Now, applying Kirchhoff Current Law at node 1, of the above circuit, we get,

From equation (i) and (ii) we get,

The open circuit voltage of both the sources is V and short circuit current of both sources is I. The same resistance connected in series in voltage source is connected in parallel in its equivalent current source.
So, these voltage source and current source are equivalent to each other.

A current source is dual form of a voltage source and a voltage source is dual form of a current source.
A voltage source can be converted into an equivalent current source and a current source can also be converted into an equivalent voltage source.
If you’d prefer a video explanation on current to voltage source conversion, take a look at the video below:
Voltage Source to Current Source Conversion
Consider a voltage source with a terminal voltage V and internal resistance r, placed in series. The current it supplies equals:

when the source of the terminals are shorted.
This current is supplied by the equivalent current source and the same resistance r will be connected across the source. The voltage source to current source conversion is shown in the following figure.

Current Source to Voltage Source Conversion
Similarly, assume a current source with the value I and internal resistance r. Now according to the Ohm’s law, the voltage across the source can be calculated as


Thus, the voltage across the source, when its terminals are open, is V.